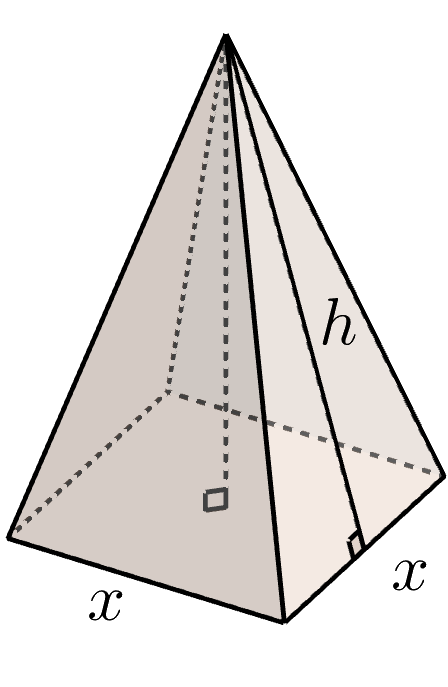
$$ SA = 4 \left( \frac{xh}{2} \right) + x^2 $$
The formula above can be used to calculate the total surface area of the right square pyramid shown, where \(x\) is the length of a side of the square base, and \(h\)
is the slant height of a lateral face.
What does the expression \(\dfrac{xh}{2}\) represent?
Using the figure and the equation, we should be able to deduce the following.
$$ SA = \underbrace{4}_\text{4 triangles} \underbrace{\left( \frac{xh}{2} \right)}_\text{area of one triangle} + \underbrace{x^2}_\text{area of square} $$
For pyramids, the lateral faces always converge upon a singular base. The name of the pyramid also denotes which face is the base.
$$ \text{right \textbf{square} pyramid} $$
Therefore, the lateral faces refer to the four triangles.